How to Test a Car Battery, Step By Step
Car batteries are essential for vehicle operation, but like everything else, eventually they fail. You’ll know this has happened when your vehicle won’t start or the motor turns over weakly. When your battery runs down and can’t start your vehicle, it’s important to determine if it’s drained and needs to be recharged, or it’s too weak to hold a charge. Sometimes low or dead batteries simply need charging or boosting. When they lose their ability to hold a charge, they need replacement.
Proper battery testing makes it easier to figure out what’s wrong with your battery. Learn how to do a detailed test of your car battery with a dedicated battery tester. You could use a multimeter, but you won’t get as much information about what’s going on inside the battery.
What you’ll need to test a car battery:
- Car battery tester
- Multimeter or voltmeter (optional)

Step 1: Avoid driving for several days, then locate the battery
- Wait at least a few days without driving to test your car battery, unless you’ve already determined it won’t start and suspect battery issues. (Your car’s alternator charges the battery while the vehicle is running. Testing the battery after not driving for a few days will tell you how well your battery is holding a charge. If it runs down significantly, it probably needs replacement.)
- Lift your vehicle’s hood when you’re ready to test the battery, if that’s where it’s housed. If not, find it elsewhere in the vehicle.
Here are 10 often-overlooked services that can extend the life of your vehicle.

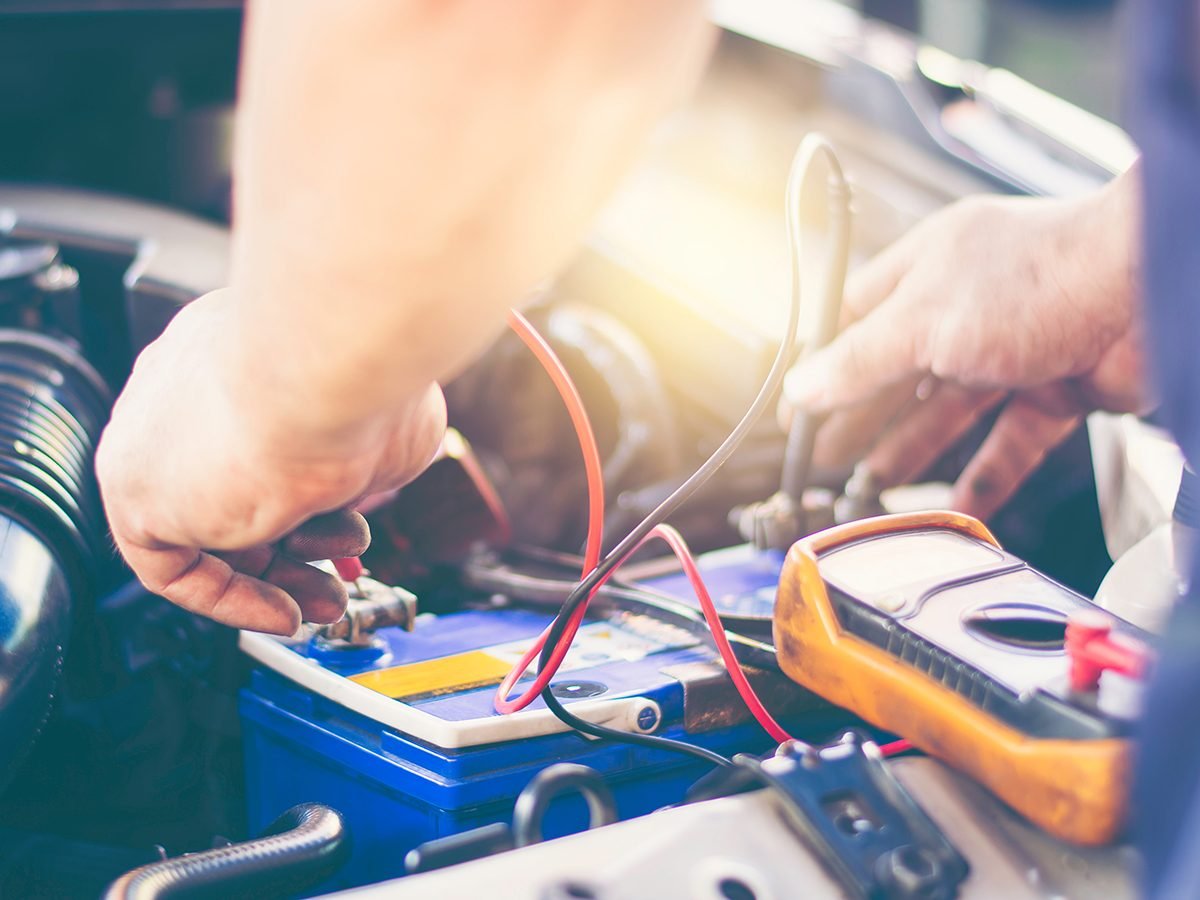
Step 2: Connect the battery tester
- Remove the red plastic protective cover from your battery’s positive terminal.
- Connect your battery tester’s red cable clip to the battery’s positive terminal.
- Connect the black cable clip to the negative terminal, then turn on the tester. (Be sure to position the tester in a spot where it sits flat and won’t fall down into the engine later when you perform cranking tests with the vehicle running. Car batteries don’t have enough voltage to electrocute you, so no need to worry about that.)

Step 3: Test voltage
- Switch your battery tester to voltage testing mode to determine the battery’s state of charge. (Most car batteries are called “12-volt,” but actual voltage depends on the state of the charge. This test can be performed with a simple voltmeter or multimeter, but a battery tester will determine this as well.)
- Determine if your battery is within the healthy voltage range. (Fully charged, it should read 12.6 volts or higher. At 12.4 volts it’ll still start your car, but is only about 75 per cent charged. If it reads 12.0 volts or lower, that’s a sign that the battery could have a weak ability to hold a charge.)
Here’s the ultimate car maintenance schedule every driver should follow.

Step 4: Test cold cranking amps
- Switch your battery tester to CCA (cold cranking amps) mode. (Cold cranking amps is a rating applied to car batteries expressing how much electricity flows from them at 0°F. Your battery’s CCA rating is probably written on its casing.)
- Input your battery’s CCA rating number into your tester. (Many testers require you to start the vehicle with the tester connected to determine actual CCA performance.)
- Compare your battery’s CCA rating with reality using your battery tester. (A healthy battery will deliver close to its rated CCA. A failing battery won’t. The tester tells you the state of battery health based on actual CCA output.)

Step 5: Perform cranking test
- Set your battery tester to cranking test mode, then start the vehicle. Your tester will record the lowest voltage that the battery is able to maintain while the starter motor is working.
- Make note of your battery’s cranking reading. (Healthy batteries should maintain between nine and 10 volts during cranking. If your test shows less than nine volts, your battery is weak.)
Check out the 20 tools no home mechanic should be without.
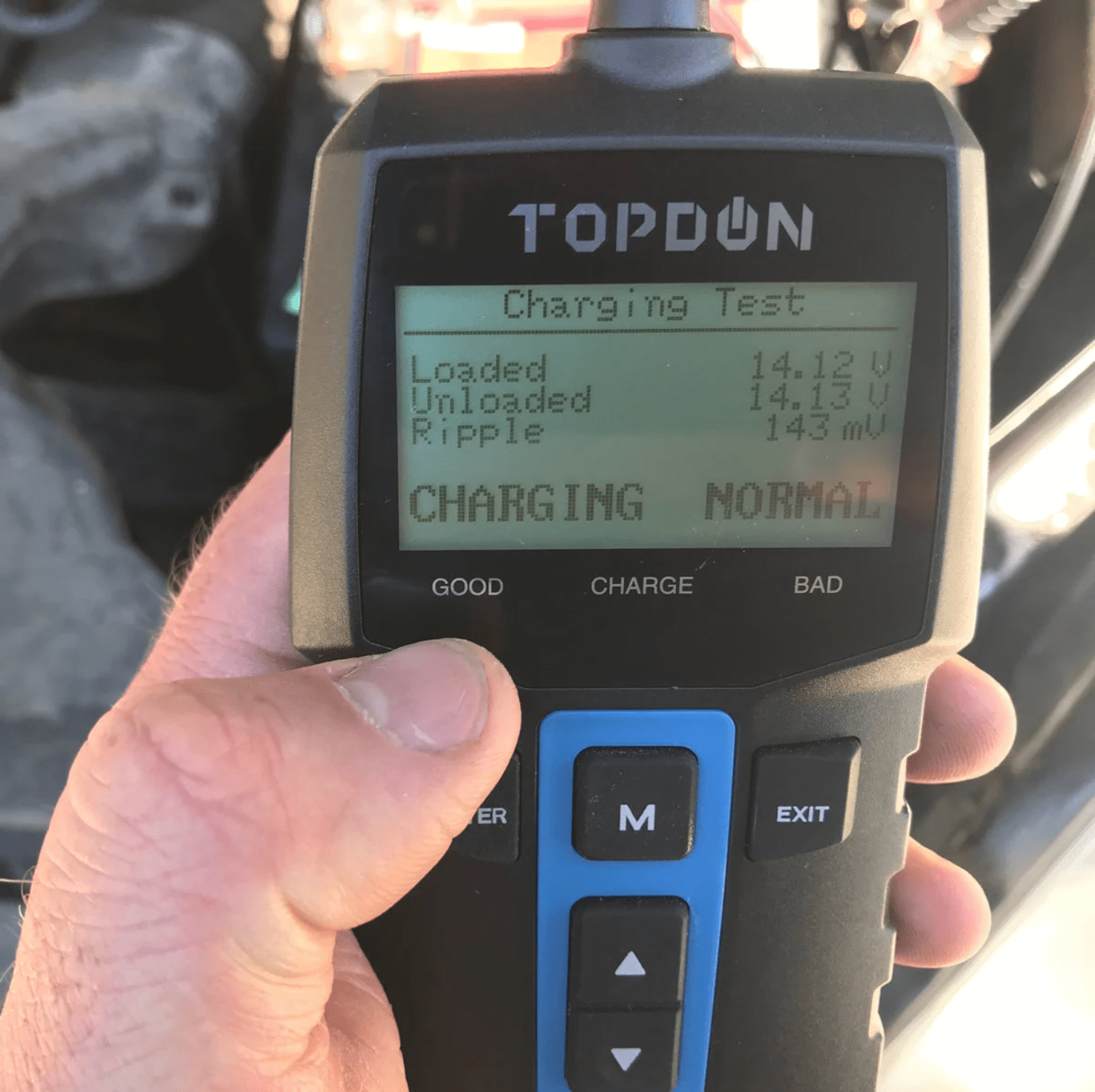
Step 6: Perform charging test
Switch your battery tester to charge testing mode with the vehicle running. If your battery and alternator are good, it should read between 14.2 and 14.5 volts. Lower than this might mean your alternator, or some other part of the charging system, needs work. This charging test can also be performed with a DC volt meter or multimeter.
Now that you know how to test a car battery, find out what these strange car noises could mean.