
Mind Trick: You Have an Unconscious “Like” Around Your Name
Science shows we show a preference for the letters that appear in our names more than other letters in the alphabet. Fascinatingly, this research also indicates which charities we’re more likely to support. In one study of Red Cross donations following tropical storms, 10 percent of all donations post-Hurricane Katrina came from people with “K” names, a group that had donated 4 percent to disasters previously. That’s a 150 percent increase!

Mind Trick: Descriptions Can Change How You Remember Things
Memory researcher Elizabeth Loftus has shown that description can distort memory through a number of different experiments, says Alter. In one fascinating study, participants watched a video of two cars colliding. Researchers told one group that the cars had hit each other, and the other group that the cars had smashed. A week later, the scientists asked participants if they recalled broken glass at the accident. Fourteen percent of those in the “hit” group remembered seeing glass, while a third of the “smashed” panel thought it was there. But really? There hadn’t been any glass. As Alter puts it, “the sensationalized ‘smashed’ label had replaced reality with a false memory in which the cars spilled glass following the accident.”
(Photo: Thinkstock)

Mind Trick: Mirrors May Make You Behave More Morally
Researchers have found that people are more honest when forced to stare at their own mirror images, Alter writes. In one mid-70s experiment, college students were asked to unscramble a series of anagrams during a five-minute period, even though there was no way they could finish all of the puzzles during that time. The participants were told to stop working after a bell rang at the five-minute mark, or it would be considered cheating. Some did the work in front of a mirror; some couldn’t see their reflections. The fascinating results: Only 7 percent of the mirror group cheated, compared to 71 percent of the other group. “When people consider behaving badly, their mirror images become moral policemen,” says Alter.
(Photo: Thinkstock)
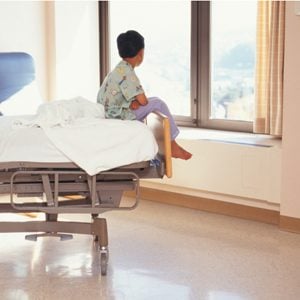
Mind Trick: Hospital Window Views Can Affect a Patient’s Recovery
Patients recovering from gallbladder surgery at a suburban Philadelphia hospital had notably different experiences, depending on whether their rooms faced a brick wall or a small group of trees. The wall-facers needed to stay in the hospital a full day longer, on average, and also had more pain and were more likely to be depressed. Very few of the patients with the tree view needed more than one dose of a strong painkiller by the middle of their visit; whereas the wall facers required two or three doses. By some measures, Alter writes, patients who gazed at a natural scene were four times better off than those who faced a wall. Other studies have found that natural environments have had positive impacts on children with ADHD. Alter explains that “while man-made landscapes bombard us with stimulation, their natural counterparts give us the chance to think as much or as little as we’d like, the opportunity to replenish exhausted mental resources.”
(Photo: Thinkstock)

Mind Trick: You Recall More in a Similar Setting
If you’ve ever heard teachers advise students to study in environments as similar to their exam room as possible, this research explains why. Researchers had scuba divers memorize lists of words, sometimes they were underwater and sometimes they were on land. They found that divers who performed the task under the sea had more accurate recall while submerged than while on land, and those who did the experiment on land remembered the words better there than under the water. “Locations form a lens through which we perceive newly acquired information,” says Alter.
(Photo: Thinkstock)

Mind Trick: Bright Pink Calms You Down
In a famous 1979 experiment, a group of healthy young men demonstrated dramatically more arm strength when they stared at a bright blue piece of cardboard compared to when they looked at a bright pink one. The study author Alexander Schauss began touting the “miraculous tranquilizing power of bright pink at public lectures across the United States,” notes Alter, and the message took off. Country jails and detention centres began to paint holding cells bubblegum pink, which became known as “drunk tank pink.” Football coaches at Colorado State and the University of Iowa even painted the visitor locker rooms pink-“in an attempt to pacify their opponents”-until athletic conferences mandated both sets of locker rooms had to be the same colour.
(Photo: Thinkstock)

Mind Trick: Hot Weather Can Make Tempers Flare
Experts believe that heat changes us physically (we sweat more, our hearts beat faster), and it’s easy to mistake this excitement for anger during frustrating situations. Heat also makes us uncomfortable, which can promote anger and aggression-for example, studies have also found road rage is more common on warm days than cool ones. Scientists have also observed that Major League Baseball batters are much more likely to be struck by errant pitches on hotter days than cooler ones. (Note: pitches were equally accurate on warm and cool days.) Separate research also noted that when a batter was hit by the opposing team, his pitcher retaliated. At a cool 55 degrees, pitchers struck back 22 percent of the time. However, on 95 degree days, pitchers let loose 27 percent of the time. It may not seem like a lot, Alter notes, but this means that “121 additional batters would be hit in retaliation if every day of the season peaked at 95 degrees rather than 55.”
(Photo: Thinkstock)