Medical trivia question #1: High-density lipoprotein is…
A. A muscle-building nutrient
B. “Good” cholesterol that reduces the risk of heart disease
C. A resilient cancer cell
D. A molecule that makes hair shiny and healthy

Answer #1: B
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is the name for “good” cholesterol that picks up excess “bad” cholesterol in the blood and takes it to the liver, where it’s broken down. HDL can be measured with a blood test. If it’s too low, exercise, quitting smoking and choosing healthy fats are good ways to raise it. How’s that for medical trivia that could save your life?
Find out the worst foods for your cholesterol.

Medical trivia question #2: Adherence is the degree to which…
A. A doctor follows medical regulations
B. A patient keeps returning to the same doctor
C. A doctor keeps track of a patient’s progress
D. A patient follows medical recommendations

Answer #2: D
Adherence is the degree to which a patient follows a doctor’s advice. Blood-pressure medication regimens, for example, are known for poor adherence because many patients underestimate the risks of hypertension.
Find out the medication mistakes that could be making you sick.
Medical trivia question #3: A keloid is…
A. A disease that mimics multiple sclerosis, causing misdiagnosis
B. An overgrowth of scar tissue
C. Fibre-rich food
D. An instrument that operating-room staff use to measure weight

Answer #3: B
A keloid is an overgrowth of scar tissue that can form after surgery or an injury. Although its lumpy or ridged tumour-like appearance can be alarming, it is usually harmless.
Here are the silent signs of cancer men are likely to ignore.

Medical trivia question #4: A zoonotic disease is an illness that…
A. Can be treated by a trained veterinarian
B. Requires animal products to eradicate
C. Can be transmitted from animals to humans
D. Threatens to wipe out a species

Answer #4: C
A zoonotic disease is an illness that can be transmitted from animals to humans. Among the more common ones is salmonella infection (from chickens, ducks, turtles, snakes).
Samonella is just one of the diseases you can prevent simply by washing your hands.
Medical trivia question #5: Orthostatic hypotension is…
A. A raised heart rate due to chronic stress
B. Light-headedness caused by a lack of sodium
C. Lowered blood pressure caused by standing up
D. Poor circulation in the hands and feet

Answer #5: C
Orthostatic hypotension is temporarily lowered blood pressure resulting from blood pooling in your legs after you stand up. It can make you feel dizzy or light-headed. If the sensation lasts beyond a few minutes or leads to fainting, it may point to a condition such as heart disease or uncontrolled diabetes.
Learn to spot the signs you might have diabetes.

Medical trivia question #6: Bromodosis is…
A. Food poisoning
B. A caffeine high
C. Stinky feet
D. A fasting regimen

Answer #6: C
Bromodosis is the medical term for stinky feet. Your feet start to smell when bacteria in your shoes or on your skin break down the sweat being produced by your feet. Since bacterial growth is optimal in damp environments, the most effective way to deal with bromodosis is to avoid wearing the same pair of shoes two days in a row, so that each pair has enough time to dry out.
Find out more home remedies for stinky feet.
Medical trivia question #7: Hyperlordosis is…
A. An over-sensitivity to bright light
B. Over-exercising
C. A sudden personality change
D. An exaggerated curve in the lower back

Answer #7: D
Hyperlordosis is an overly accentuated inward curve in the lower back. Its risk factors include obesity, hip disorders and the inflammation of intervertebral discs. It can lead to back pain but can be counteracted by core- and buttock-strengthening exercises, as well as by making a conscious effort to maintain good posture.
Here’s another bit of medical trivia you probably didn’t know: It turns out men can also benefit from kegel exercises.

Medical trivia question #8: Black carbon is…
A. An air pollutant emitted by vehicles
B. A toxin found in diseased potatoes
C. A noxious fume produced by malfunctioning home-heating systems
D. A suspected carcinogenic component of mobile phones

Answer #8: A
Black carbon is an air pollutant associated with respiratory and cardiovascular health problems, as well as climate change. In Western countries, vehicles are the main source, especially those with diesel engines. To minimize exposure, individuals can avoid walking near heavy traffic, while governments can pass regulations to improve air quality.
Follow our healthy home checklist for tips on how to improve your indoor air quality.

Medical trivia question #9: Idiopathies are…
A. A family of mental disorders marked by an unremitting obsession with privacy
B. Conditions that eventually lead to cognitive decline
C. Diseases of unknown origins
D. A series of opportunistic bacterial infections

Answer #9: C
Idiopathies are diseases of unknown origins. For example, you might be diagnosed with idiopathic hypersomnia if the causes for your excessive daytime sleepiness are unclear, or with idiopathic urticaria if you have recurring hives for no apparent reason.

Medical trivia question #10: An iatrogenic health problem…
A. Is nonfatal but incurable
B. Was inadvertently caused by medical treatment
C. Stems from chronic stress
D. Is present at birth
Answer #10: B
Health problems are called “iatrogenic” when they were accidentally caused by medical treatment. These include infections contracted from other people being treated at the hospital, medication side effects and surgery complications. Patients should always feel free to ask their doctors about the risks of proposed treatments.
Here are the questions you must always ask when picking up a new prescription.

A trace mineral is one that…
A. Is possible to measure in the body
B. Is suspected of contributing to heart disease
C. Is commonly found in tap water
D. Is needed only in tiny amounts to maintain health

Answer: D
Trace minerals are those that the body needs only in miniscule quantities. They include chromium, copper, selenium, sulfur and zinc. Most people can get the required dose from their food.
Find out which vitamins and supplements should always be taken with food.

Malabsorption is when…
A. The brain doesn’t retain new information
B. A drug shows no effects
C. The blood fails to clot in a wound
D. The body has trouble taking in nutrients from food

Answer: D
Malabsorption is an impairment of the body’s ability to get nutrients from food. It can lead to weight loss, bloating, diarrhea, muscle wasting or gas and is caused by conditions such as Crohn’s and liver disease. Malabsorption can also be a side effect of medications.
Learn to spot the symptoms of a nutrient deficiency.

Brassica oleracea is a….
A. Hair-growth disorder
B. Shoulder bone that is prone to fractures
C. Gene associated with aggressive breast cancer
D. Vegetable species

Answer: D
Cabbage, kale cauliflower, broccoli and Brussels sprouts are all varieties of the same species, Brassica oleracea. They’re thought to provide protection against various cancers and are a good source of vitamins and dietary fibre. (Find out the best high-fibre foods worth adding to your diet.) When consumed regularly as staple foods, they can promote goitre (a swollen thyroid gland), but usually only in people who are already deficient in iodine.
The “recovery position” is the recommended posture for…
A. Placing someone who is unconscious but breathing
B. Healing from surgery
C. Slowing one’s heart rate after exercise
D. Sitting with an injured ankle
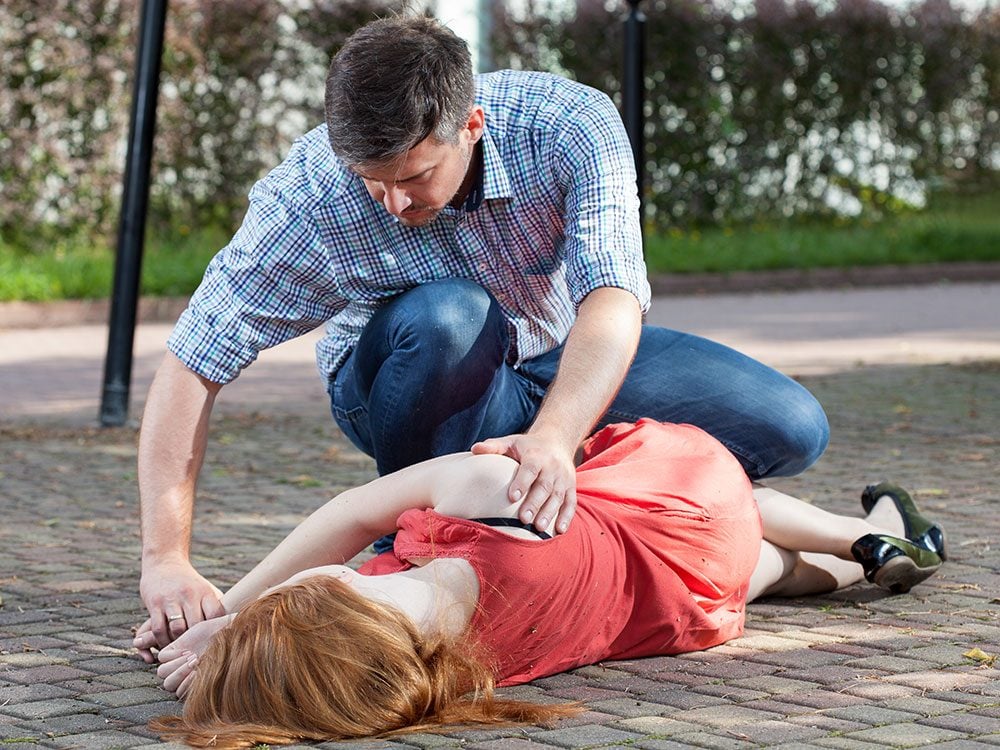

Answer: A
In first aid, the recovery position is for people who are unconscious but breathing and free from spinal injuries. By rolling the victim onto their side, one ensures that saliva or vomit won’t obstruct the airways.
If you didn’t get this medical trivia question right, you might want to brush up on the seven steps of CPR.
Peak bone mass is the…
A. Best possible score on a bone mineral density test
B. Greatest amount of bone tissue a person accumulates at one point in a lifetime
C. Highest frame-size category in BMI measurements
D. The force a bone could withstand before fracturing

Answer: B
Peak bone mass is the greatest bone size and strength someone reaches in a lifetime. It generally occurs before age 30, and the higher it is, the lower the risk of osteoporosis later on. Adequate calcium intake and regular weight-bearing exercise are thought to slow down the rate of bone decay at any age.
Learn how to recognize the signs of calcium deficiency.

Aspergillus is a…
A. Genus of mould
B. Mild developmental disorder
C. Bone in the knee
D. Type of antibiotic
Answer: A
Aspergillus is a mould that is normally harmless because our immune system can deal with it readily. However, it sometimes causes wheezing, coughing or even life-threatening breathing issues in people with asthma, cystic fibrosis or weakened immune function. The mould is almost impossible to avoid: it may be found in rotting leaves, compost, air conditioning and heating systems, insulation, food and dust. Reactions can be treated with corticosteroids and antifungal medications.
Find out eight science-backed ways to boost your immune system.

Anosmia is…
A. Colour-blindness
B. Confusion brought on by lack of sleep
C. A lack of zinc
D. An inability to smell
Answer: D
Anosmia is the medical term for the loss of the sense of smell. It can be a symptom of COVID-19 or an early symptom in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s, though it’s more commonly caused by a nasal problem (such as a cold) or a brain injury. Patients with long-lasting or permanent anosmia should take precautions because they can’t smell fires, gas leaks or food that has gone bad.
Here are the early signs of Parkinson’s you might be ignoring.

The thymus is…
A. The centre of a wart
B. The sphincter between the large and small intestines
C. A gland in the upper chest
D. Part of the brain involved with self-consciousness

Answer: C
Located just behind the breastbone, the thymus gland helps with the maturation of T cells, an important part of the immune system. Unfortunately, the thymus can develop cancer. Signs of a tumour can include shortness of breath, high-pitched breathing noises, chest pain and coughing, sometimes with blood.
Here’s how to tell which cancer screenings you really need.

Cholecystitis is an…
A. Ear infection
B. Enlarged kidney
C. Infestation of head lice
D. Inflamed gallbladder
Answer: D
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. It’s most commonly caused when gallstones—which are found in around 10 per cent of adults—block the gallbladder’s main opening, trapping bile inside. When gallstones cause cholecystitis, the condition usually needs to be treated in hospital, possibly with surgery.
Don’t miss these expert tips on how to prevent gallstones.
A chalazion is a…
A. Benign genetic anomaly
B. Cramp in the foot
C. Person with two different blood types
D. Lump in the eyelid

Answer: D
A chalazion is a lump-like cyst that appears in the eyelid, usually because the oil-producing glands are blocked. This common problem often goes away by itself, but you can help the healing process along by holding a clean cloth soaked in hot water over the eye for five to 10 minutes three to four times a day.
Here are the signs you need to see an eye doctor.
The sinus node is the…
A. Group of cells that regulate the heartbeat
B. Place where the sinuses connect to the nasal cavity
C. Organ that produces mucus in the nose
D. Topmost vertebra on the spine

Answer: A
Also called the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinus node is a collection of cells in the right atrium that control the heart’s rhythm by sending out electrical impulses. When the sinus node doesn’t work properly, the pulse can become too fast, too slow or irregular.
Check out 50 heart health tips cardiologists want you to know.

Hirsutism is…
A. Sun spots
B. An overactive immune system
C. The inability to feel hungry
D. Male-pattern hair growth in women

Answer: D
Hirsutism is excessive female hair growth in areas where hair is more typically visible in men: the face, neck, back, chest, belly and so on. Involving a surplus of androgens, hirsutism can be caused by heredity or menopause, but it can also point to polycystic ovary syndrome or a tumour on the adrenal glands.
For more medical trivia you didn’t know you needed to know, find out the sneaky reasons your hair is falling out.
EQ-5D is…
A. A gene that contributes to nearsightedness
B. An emotional-intelligence test
C. An active compound in fertility medications
D. A survey for measuring health-related quality of life

Answer: D
The EQ-5D is a standardized, international questionnaire used for measuring general health and quality of life. It spans five dimensions: mobility, usual activities, pain/discomfort, self-care and anxiety/depression. The questionnaire can be used in research to find out how a given factor—medical condition or a new treatment, for instance—affects health status.
Want to improve your score? Find out what happens to your body when you start walking 10,000 steps a day.

A ferritin test measures…
A. The severity of an immune reaction
B. Iron in the blood
C. The body’s metabolic rate
D. Spatial intelligence
Answer: B
A ferritin test measures the amount of ferritin—a protein that contains iron—in your blood. If levels are low, your doctor may diagnose you with iron deficiency. A higher-than-normal result could point to liver disease, hyperthyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, Hodgkin’s lymphoma or various other conditions.
Concerned about low iron? Consider adding these iron rich foods to your diet.
Catecholamines are…
A. Medications that inhibit allergies
B. Hormones secreted by the inner adrenal glands
C. Mineral salts present in the blood plasma
D. Scar tissues

Answer: B
Catecholamines are hormones that are made by the adrenal glands when a person is under physical or emotional stress. They include dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine (also known as adrenaline). Doctors can measure for them with a blood or urine test, and higher-than-normal levels can indicate anxiety or a tumour.
Learn to spot the silent signs of high-functioning anxiety.

Paresthesia is…
A. Temporary paralysis
B. A tingling sensation in a limb
C. When different bodily senses conflate in the mind
D. An addiction to plastic surgery
Answer: B
Also known as “pins and needles,” paresthesia is a tingling, pricking or numb sensation that usually arises in the arms, legs, hands or feet. Long-lasting paresthesia could be a sign of many different underlying conditions, including multiple sclerosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, diabetes or sciatica.
These 1o foot symptoms could signal a serious disease.

Lactase is…
A. A micronutrient found in dairy products that helps build muscle mass
B. When a mother stops producing milk after weaning her child
C. An enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk
D. A disorder affecting infants who lack the instinct to breastfeed

Answer: C
Lactase is a digestive enzyme that helps break down milk sugars. Virtually all humans produce plenty of lactase as babies, but many decrease production in adulthood. In fact, only about a third of the world’s adults can fully digest dairy. Genes play a large role in lactase persistence: for instance, roughly 25 per cent of Greek adults can consume lactose without effects such as gas or bloating, compared to upward of 90 per cent of Irish men and women.
Check out the latest research on the growing debate: is milk good for you?

Capillary refill time is the time it takes for…
A. One of the heart’s ventricles to fill with blood following a contraction
B. Colour to return to the nails after they’ve been pinched
C. The bladder to fill up after emptying
D. A prescription drug to be available after a shortage
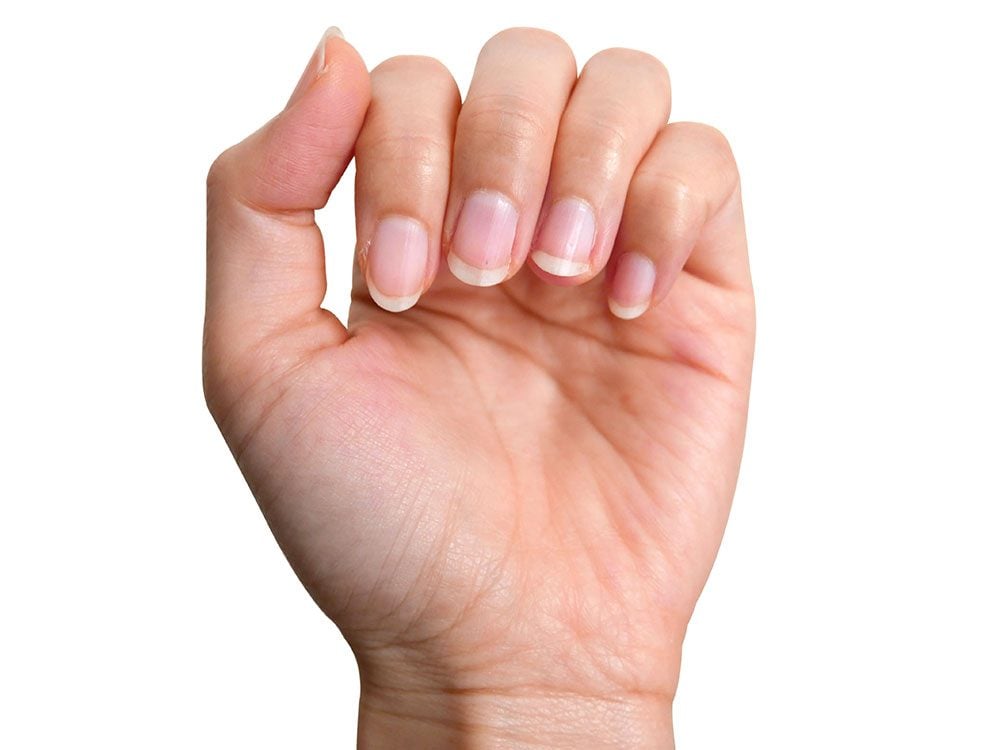

Answer: B
Capillary refill time refers to how long it takes for a nail to regain colour after pressure is applied and released. It can be used to measure the strength of blood circulation, since the fingers and toes are far from the heart. Normally, colour returns within two seconds.

The Framingham risk score is…
A. The probability of a mother passing an infection on to her child during birth
B. A quantification of risky alcohol habits
C. A measure of a patient’s knowledge about preventing sexually transmitted infections
D. A tool for assessing risk of cardiovascular disease
Answer: D
The Framingham risk score estimates a patient’s chances of developing cardiovascular disease within the next 10 years. It does so based on age, sex, cholesterol levels, diabetes status, blood pressure and smoking habits. Patients and doctors use the score to decide whether lifestyle changes or preventative treatments would be worthwhile.
Find out five more heart tests that could save your life.
Radiofrequency ablation is…
A. A constellation of symptoms resulting from nuclear radiation
B. Sensitivity to noise
C. Monitoring patients remotely via computer
D. A treatment that uses radio waves to heat tissues
Answer: D
Radiofrequency ablation is a non-surgical treatment for back pain, neck pain or chronic arthritis. Delivered by a needle, a radiofrequency current heats nerve tissues, interrupting the pain signals they were sending to the brain. The nerve will likely regenerate in time, but pain relief may last up to 12 months. It’s considered a low-risk treatment, though it can occasionally result in infection or bleeding at the treated site.
Check out five sneaky reasons you’re suffering from back pain (and how to find relief).

Antiemetics are drugs that prevent or reduce…
A. Fainting
B. The spread of infection
C. Nausea and vomiting
D. Muscle aches and pains

Answer: C
An antiemetic is a drug that can stop or diminish nausea and vomiting. There are many antiemetics, and the most appropriate ones to use depend on the cause of the symptoms. Common examples include dimenhydrinate (Gravol) for motion sickness, palonosetron (Aloxi) for chemotherapy-related nausea and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) for the stomach flu.

Relative fat mass (RFM) is…
A. When obesity runs in a family for genetic reasons
B. A method for monitoring changes in body weight
C. The proportion of a food’s mass that consists of fat
D. An equation for estimating body-fat percentage

Answer: D
Relative fat mass is a new way of estimating the percentage of your body that is made up of fat. Based on the ratio between your height and the circumference of your waist, RFM has been shown to be more accurate than body mass index (BMI) for making this estimation and ascribing the right obesity category.

Radiofrequency energy (RFE) is a form of radiation notably given off by…
A. MRI machines
B. Mobile phones
C. CT scanners
D. The sun

Answer: B
RFE (also known as radio waves) is a type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by cellphones. Like microwaves, and unlike ultraviolet or X-rays, it operates at a frequency too low to damage cells by ionizing atoms. Some people nevertheless worry that RFE could cause cancer or other conditions. So far, no reliable evidence exists for a link between cellphone use and health problems, but more research is needed.
Just how clean is your phone? According to research, it’s one of the filthiest things you touch every day.

Extrinsic aging is…
A. Toxic mould growth on old food
B. When ultraviolet radiation damages the skin
C. Cellular degradation due to chronic stress
D. The overall effect of aging on quality of life

Answer: B
Extrinsic aging is skin damage caused by environmental factors, primarily UV radiation, as opposed to the unavoidable changes related to genetics and passing time. On exposed skin, up to 90 per cent of aging can be caused by the sun or tanning booths. To see the extent to which this may be happening to you, compare regularly exposed areas (the face and neck, for example) to areas that are usually covered. Unlike natural skin aging, extrinsic aging can cause a leathery texture, spider veins, freckling, discolouration and deep wrinkles.
Boost your skin’s protection with these summer sunscreen tips.

A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary…
A. Heart stoppage
B. Inability to breathe
C. Blood-pressure spike
D. Blockage of the brain’s blood supply

Answer: D
A transient ischemic attack, also known as a mini-stroke, is a temporary disruption of the blood flow to the brain, possibly marked by numbness or paralysis in the face or limbs, vision disturbance, a severe headache or trouble speaking and understanding speech. Although symptoms usually last for only a few minutes, see a doctor right away if they occur. A TIA is a sign of plaque, clotting or other obstructions in the arteries leading to your brain.
Find out how to reverse heart disease.
A cervical rib is…
A. An extra rib near the neck
B. A benign, narrow cyst on the cervix
C. A tool for taking Pap test samples
D. A broken rib that threatens to puncture the lungs
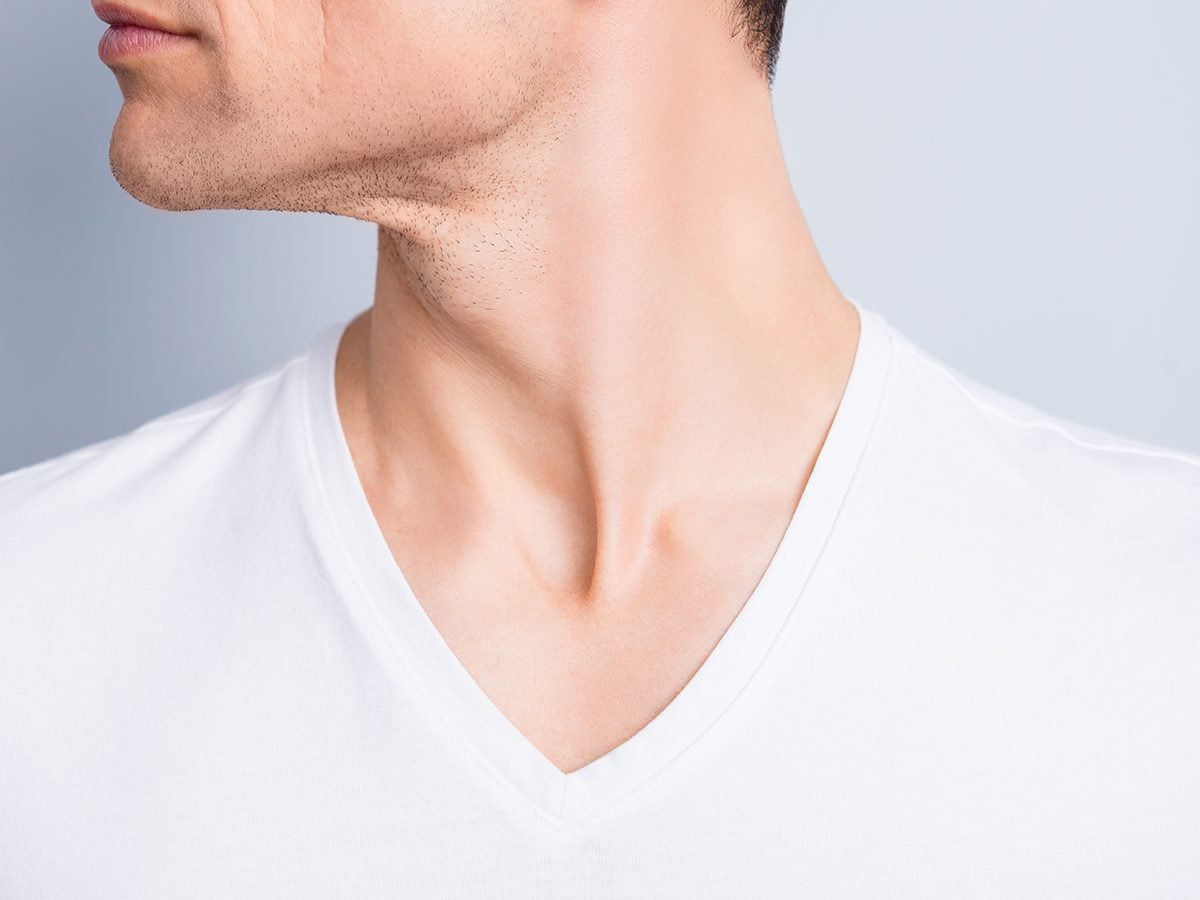
Answer: A
At least one in every 500 people has an extra rib on one or both sides of the neck’s base, just above the collarbone. Known as cervical ribs, these bones are visible in imaging tests and won’t necessarily cause any trouble. Sometimes, however, they compress nerves or blood vessels, causing pain in the neck or shoulders, arm numbness or finger tingling. Physical therapy may remedy their unwanted effects; if not, they can be surgically removed.
Here are more weird body parts you didn’t know you had!

Polymorphous light eruption is…
A. A rash triggered by sunlight
B. When acne medication backfires, worsening an outbreak
C. Gas caused by eating too quickly
D. An asthma flare-up due to volcanic debris in the air

Answer: A
Polymorphous light eruption is a bumpy or patchy rash that is triggered by the sun. (It’s an immune-system reaction, not a sunburn.) It’s most likely to happen after one of your first substantial exposures to sunlight in a long while and normally clears up within two weeks. Until then, avoid the sun, cover up with clothing or wear high-SPF sunscreen.
Here are four skin changes you should never ignore.

Secondary Parkinsonism is…
A. Parkinson’s disease that progresses more slowly than usual
B. Lesser-known Parkinson’s symptoms, such as anxiety or a lost sense of smell
C. The indirect effects of Parkinson’s disease upon caregivers
D. Parkinson’s-type symptoms that are not due to Parkinson’s disease

Answer: D
Secondary Parkinsonism is when someone does not have Parkinson’s disease but nevertheless has tremors, stiffness or slowness. It can result from conditions such as meningitis, stroke or diffuse Lewy body disease (a type of dementia). It can also be caused by substances, such as antipsychotics or certain nausea drugs. Secondary Parkinsonism is hard to distinguish from Parkinson’s but will not respond as well to the same treatments.
If you enjoyed this medical trivia challenge, see how you fare on our quiz of first aid terms.